The Future of Fiber Optic Patch Cord Connectors: FC/UPC vs FC/APC
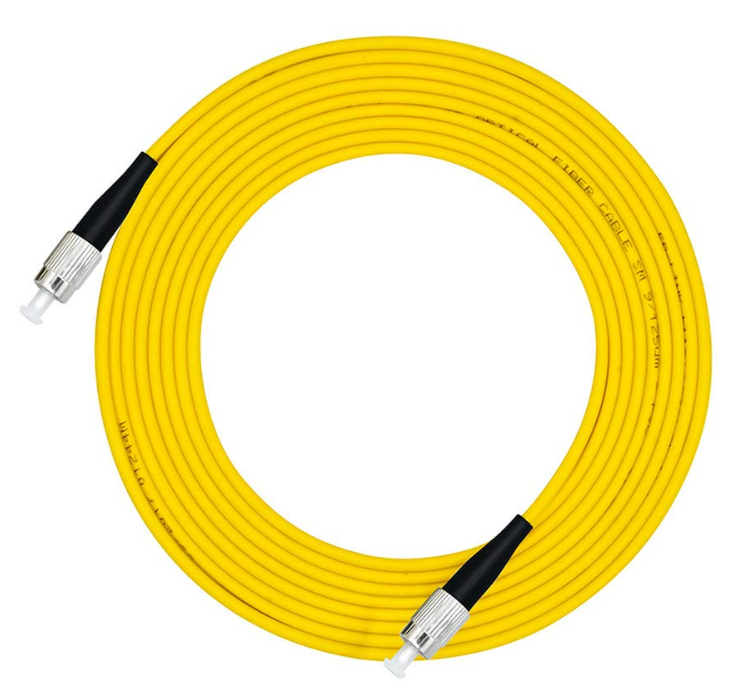

Exploring FC/UPC and FC/APC Fiber Optic Patch Cord Connectors
Fiber optic patch cord connectors play a crucial role in ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission. Two popular options in the market are FC/UPC and FC/APC connectors. Understanding the key differences between these connectors is essential for making informed decisions when it comes to choosing the right connector for your specific needs.
FC/UPC (Ferrule Connector/Ultra Physical Contact) and FC/APC (Ferrule Connector/Angle Physical Contact) connectors differ primarily in their endface polish, which affects their optical performance. The FC/UPC connector features a flat, polished endface, while the FC/APC connector has an angled endface. This variation impacts factors such as insertion loss and return loss.
Both types of connectors have their advantages and disadvantages. By exploring these aspects, we can gain insights into which connector may be more suitable for different applications. Additionally, understanding the applications of FC/UPC and FC/APC connectors across various industries helps us appreciate their versatility.
What are FC/UPC and FC/APC Connectors?
Understanding FC/UPC Connectors
FC/UPC connectors, also known as Ferrule Connector/Ultra Physical Contact connectors, are widely used in fiber optic networks. These connectors feature a flat, polished endface that ensures precise alignment and low insertion loss. The purpose of FC/UPC connectors is to provide a reliable connection between fiber optic cables.
One of the key features of FC/UPC connectors is their compatibility with various fiber types, including single-mode and multimode fibers. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as telecommunications, data centers, and broadcast.
The characteristics of FC/UPC connectors include high return loss and low insertion loss. The high return loss ensures minimal signal reflection, resulting in improved signal quality. Additionally, the low insertion loss minimizes signal attenuation during transmission.
Exploring FC/APC Connectors
FC/APC connectors, or Ferrule Connector/Angle Physical Contact connectors, are similar to FC/UPC connectors but differ in their endface polish. The endface of an FC/APC connector is angled at 8 degrees to minimize back reflections and improve optical performance.
The purpose of FC/APC connectors is to achieve superior return loss and low back reflection levels. These connectors are ideal for applications that require high precision and minimal signal degradation, such as long-haul communications and fiber optic sensing systems.
The features and characteristics of FC/APC connectors make them suitable for demanding environments where signal integrity is critical. However, it's important to note that terminating and installing FC/APC connectors can be more challenging compared to FC/UPC connectors due to the angled endface.
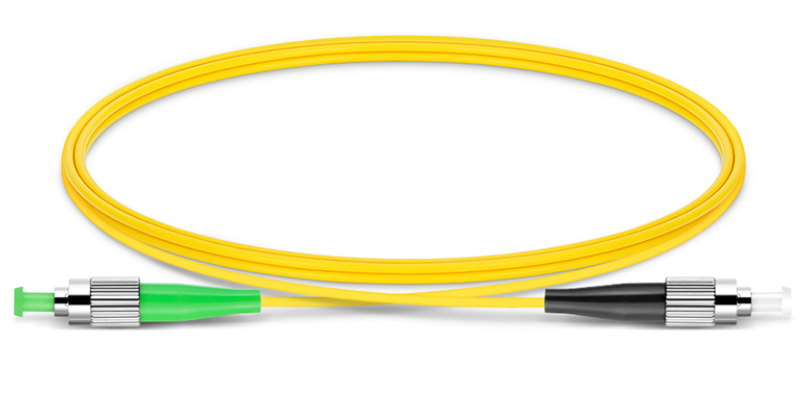
Comparing FC/UPC and FC/APC Connectors
Physical Differences
When comparing FC/UPC and FC/APC connectors, there are noticeable variations in their design and appearance. The FC/UPC connector typically features a flat endface, while the FC/APC connector has an angled endface. This difference in endface polish is crucial for optimizing optical performance.
The flat endface of the FC/UPC connector allows for precise alignment with the mating connector, ensuring minimal signal loss during transmission. On the other hand, the angled endface of the FC/APC connector reduces back reflections by directing them away from the source, resulting in improved return loss.
In terms of appearance, the angled endface of the FC/APC connector can be easily identified by its green color, which indicates its angle-polished nature. In contrast, the flat endface of the FC/UPC connector is typically colorless or blue.
Optical Performance
The type of connector used can significantly impact optical performance in fiber optic networks. Insertion loss refers to the amount of signal power lost when light passes through a connection point. Both FC/UPC and FC/APC connectors offer low insertion loss; however, due to its angled endface, the FC/APC connector generally provides slightly lower insertion loss compared to the FC/UPC connector.
Return loss measures how much light is reflected back towards its source at a connection point. The angled endface of the FC/APC connector greatly reduces back reflections and results in superior return loss compared to the flat endface of the FC/UPC connector.
Understanding these physical differences and their impact on optical performance is essential when selecting connectors for specific applications. Factors such as insertion loss and return loss requirements should be carefully considered to ensure optimal signal quality in fiber optic systems.
Pros and Cons of FC/UPC and FC/APC Connectors
Advantages of FC/UPC Connectors
FC/UPC connectors offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in fiber optic patch cord applications. One key advantage is their high return loss and low insertion loss, which ensures minimal signal degradation during transmission. This makes them suitable for demanding environments where signal integrity is crucial.
Another advantage of FC/UPC connectors is their compatibility with various fiber types, including single-mode and multimode fibers. This versatility allows for flexibility in network design and implementation, making them widely applicable across different industries.
Disadvantages of FC/UPC Connectors
Despite their advantages, FC/UPC connectors have a few limitations. In high-power applications, such as those involving lasers or amplifiers, FC/UPC connectors may have limited performance due to the potential for increased signal power loss. Additionally, these connectors are susceptible to dust and debris accumulation, which can affect their performance over time. Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary to maintain optimal functionality.
Advantages of FC/APC Connectors
FC/APC connectors offer distinct advantages that make them suitable for specific applications. Their angled endface design provides superior return loss and low back reflection levels compared to FC/UPC connectors. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high precision and minimal signal degradation, such as long-haul communications or fiber optic sensing systems.
Disadvantages of FC/APC Connectors
While offering superior optical performance, FC/APC connectors do have a couple of disadvantages worth considering. Firstly, they tend to be more expensive than FC/UPC connectors due to the additional manufacturing process required for the angled endface polish. Secondly, terminating and installing FC/APC connectors can be more challenging due to the precise alignment required between the connector's angled endface and the mating connector.
Best Practices for Installing and Maintaining FC/UPC and FC/APC Connectors
Installation Tips for FC/UPC Connectors
Proper installation of FC/UPC connectors is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliable connections. Here are some key tips to follow:
Begin by preparing the fiber cable, ensuring it is clean and free from any contaminants or debris.
Carefully strip the fiber cable jacket using appropriate tools, taking care not to damage the underlying fibers.
Clean the fiber endface using lint-free wipes and a suitable cleaning solution to remove any dirt or oils.
Align the stripped fiber with the connector ferrule, making sure they are properly aligned before securing them together.
Apply epoxy or adhesive as per manufacturer's instructions to secure the connection between the fiber and connector.
Allow sufficient time for the epoxy or adhesive to cure before handling or testing the connector.
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential for maintaining FC/UPC connectors. Inspect connectors periodically for signs of contamination or damage, such as scratches or cracks. Clean connectors using approved cleaning techniques, such as dry cleaning methods or wet cleaning with appropriate solvents.
Maintenance Guidelines for FC/APC Connectors
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of FC/APC connectors, it is important to follow proper maintenance guidelines:
Prevent contamination by keeping connectors covered when not in use and avoiding contact with dirty surfaces.
Handle connectors with care, avoiding excessive force or bending that could cause damage.
Regularly inspect connectors for signs of contamination, such as dust, oil, or fingerprints.
Clean contaminated connectors using lint-free wipes moistened with an approved solvent specifically designed for fiber optic cleaning.
Gently wipe the endface in a circular motion while applying minimal pressure to avoid scratching.
By following these best practices for installation and maintenance, you can ensure that your FC/UPC and FC/APC connectors perform optimally and maintain reliable connections in your fiber optic network.

The Future of Fiber Optic Patch Cord Connectors
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The field of fiber optic patch cord connectors is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the demands of various industries. Here are some emerging trends and innovations to watch out for:
Advancements in connector technology: Manufacturers are continuously improving connector designs to enhance performance and reliability. This includes developing new materials with improved mechanical properties, such as increased durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Impact of industry demands on connector development: As industries continue to demand higher data rates, increased bandwidth, and improved signal quality, connector manufacturers are working towards developing connectors that can meet these requirements. This involves optimizing connector design, reducing insertion loss, and minimizing back reflections.
Future Applications
The future holds exciting potential for fiber optic patch cord connectors across various applications. Some anticipated developments include:
Potential uses of fiber optic patch cord connectors: With the increasing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart cities, and 5G networks, the demand for reliable and high-speed connectivity is growing rapidly. Fiber optic patch cord connectors will play a vital role in connecting these devices and networks, enabling seamless communication.
Anticipated developments in connector standards: As technology advances, industry standards for fiber optic connectors may evolve to accommodate new requirements. These developments could include higher power handling capabilities, improved backward compatibility with existing systems, or enhanced ease of installation.
As the world becomes increasingly connected and data-intensive applications continue to expand, the future of fiber optic patch cord connectors looks promising. Staying informed about emerging trends and advancements in this field will be crucial for professionals working with fiber optic networks.
Embracing the Future of Fiber Optic Patch Cord Connectors
As we look ahead to the future of fiber optic patch cord connectors, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your application. Whether you choose FC/UPC or FC/APC connectors, understanding their advantages and disadvantages will help you make an informed decision.
Following best practices for installation and maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your fiber optic patch cord connectors. Regular cleaning, inspection, and adherence to proper handling techniques will help maintain reliable connections.
Lastly, staying informed about emerging trends and advancements in fiber optic patch cord connectors is essential. The industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and standards being developed. By keeping up-to-date with these developments, you can ensure that your network remains efficient and future-ready.
See Also
Innovative Wall Mount Solutions and Trends for Fiber Optic Patch Panels
LSZH Fiber Optic Patch Cords: Promoting Safety and Sustainability
High-Speed Data Transmission: OM4 MTP/MTP 12 Strand Multi-Fiber Patch Cables Unleashed
Advancements in Fiber Optic Patch Cord Technology in FTTX and FTTH Networks


