A Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Pigtail: LC, ST, and SC Connectors
Understanding Fiber Pigtails
Exploring Fiber Optic Connectors
Fiber pigtails are an integral part of fiber optic networks, serving as the connection between the fiber cable and the network's equipment. The differences between LC, ST, and SC connectors are crucial for various applications in networking. Understanding these differences is essential for choosing the right connector to ensure seamless connectivity and optimal network performance.
When it comes to fiber optic networks, the type of connector used can significantly impact the network's efficiency and reliability. Let's explore the distinct characteristics and applications of LC, ST, and SC connectors in more detail.
Exploring Fiber Optic Connectors
Types of Connectors
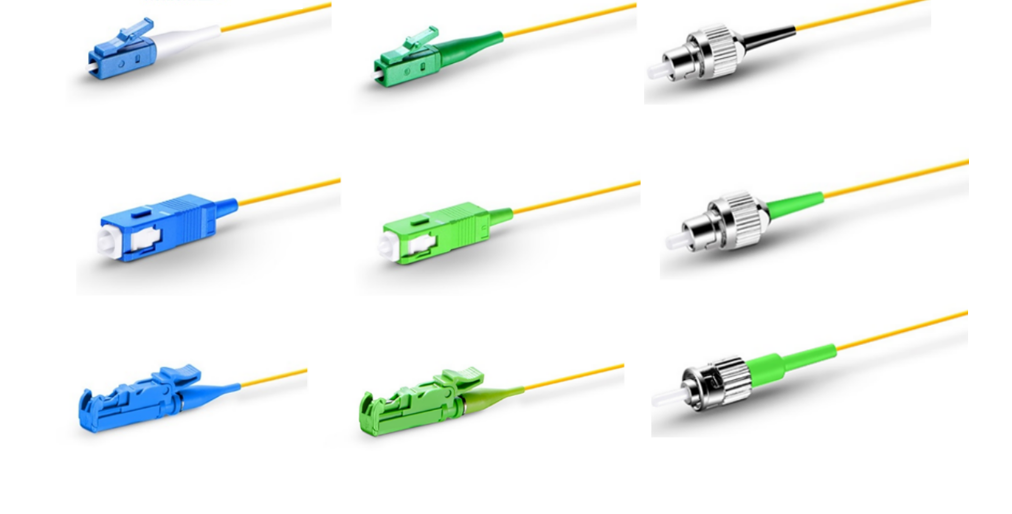
In fiber optic networks, various types of connectors are utilized to facilitate the seamless transmission of data. The LC, ST, and SC connectors are among the most widely used options, each with its distinct characteristics and applications.
The LC connector is known for its small form factor, making it ideal for high-density connections in data centers and telecommunication rooms. Its push-pull design allows for easy insertion and removal, making it a popular choice for network engineers.
On the other hand, the ST connector features a bayonet-style coupling mechanism, providing a secure connection suitable for harsh environmental conditions. It is commonly used in industrial and manufacturing settings where ruggedness is essential.
Lastly, the SC connector offers high precision alignment with its square shape, ensuring low signal loss. This connector is often preferred in cable television and internet applications due to its excellent performance.
Understanding the differences between these connectors is crucial when designing and implementing fiber optic networks. Each type has its unique advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered based on specific network requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each type of connector has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that influence their suitability for different applications. For instance:
The LC connector's compact size enables high-density connections but may be more delicate compared to other options.
The ST connector's robustness makes it suitable for harsh environments but may not support the same level of density as the LC connector.
The SC connector's precise alignment ensures low signal loss but may require more space due to its square shape.
Careful consideration of these factors is essential when selecting the appropriate connectors to ensure optimal performance in fiber optic networks.
LC, ST, and SC Fiber Pigtails
Characteristics of LC, ST, and SC Pigtails
When it comes to the characteristics of LC, ST, and SC fiber pigtails, each type offers unique features that cater to different network requirements:
LC Fiber Pigtails:
LC fiber pigtails are known for their small form factor, similar to the LC connector. This compact size allows for high-density connections in limited spaces, making them ideal for applications in data centers and telecommunications.
The LC optical fiber pigtail is designed with a push-pull mechanism, enabling easy installation and removal without compromising on performance.
ST Fiber Pigtails:
ST fiber pigtails feature a bayonet-style coupling mechanism similar to the ST connector. This design provides a secure and robust connection suitable for harsh environmental conditions such as industrial settings.
The ruggedness of ST fiber cable pigtails makes them resilient against mechanical stress and environmental factors.
SC Fiber Pigtails:
SC fiber pigtails are characterized by their square shape, which allows for precise alignment and low signal loss. This feature makes them well-suited for applications in cable television and internet networks where signal integrity is crucial.
Understanding these distinct characteristics is essential when selecting the appropriate fiber pigtail for specific network requirements. Whether it's high-density connections in data centers or resilience in harsh environments, each type of pigtail offers unique advantages based on its design and construction.
Applications in Networks
The applications of LC, ST, and SC pigtails span across various network setups:
LC Fiber Pigtails:
Ideal for high-density connections in data centers and telecommunication rooms.
Suitable for scenarios requiring space-efficient solutions without compromising on performance.
ST Fiber Pigtails:
Commonly used in industrial and manufacturing environments where ruggedness is essential.
Well-suited for applications that demand a secure connection capable of withstanding harsh conditions.
SC Fiber Pigtails:
Preferred in cable television and internet applications due to their precise alignment capabilities.
Suitable for scenarios where low signal loss is critical to maintaining optimal network performance.
By understanding these applications, network professionals can make informed decisions when integrating LC, ST, or SC pigtails into their network designs. Each type offers specific benefits tailored to diverse networking needs.
Fiber Termination Methods
Termination Techniques
When it comes to connecting fiber pigtails to optical fibers, various termination techniques are employed to ensure reliable and efficient connections. Two commonly used methods for fiber cable termination include fusion splicing and mechanical splicing.
Fusion Splicing:
Fusion splicing involves fusing or welding the ends of two optical fibers together using an electric arc. This method results in a low-loss connection with minimal reflectance, making it ideal for high-performance networks. Fusion splicing is particularly suitable for long-haul telecommunications and undersea fiber optic cable systems where signal integrity is paramount.
Mechanical Splicing:
In contrast, mechanical splicing utilizes precisely aligned fiber alignment fixtures to join optical fibers without welding. While not as low-loss as fusion splicing, mechanical splicing offers the advantage of being quicker and more cost-effective, making it suitable for certain network setups.
Best Practices
Adhering to best practices for fiber termination is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in fiber optic networks. Some key best practices include:
Maintaining cleanliness during the termination process to minimize signal loss.
Ensuring proper alignment and securely fixing the terminated fibers to prevent any movement.
Conducting thorough testing post-termination to validate the quality of the connection.
By following these best practices, network professionals can ensure that their fiber terminations meet industry standards and deliver consistent performance in diverse network environments.
Applications and Significance in Networks
Network Deployment
In the realm of network deployment, fiber optic pigtails play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient data transmission. These essential components serve as the bridge between the fiber cables and the network equipment, facilitating the smooth flow of information within the network infrastructure.
The significance of fiber cable pigtails in network deployment cannot be overstated. They are instrumental in establishing reliable connections, whether it's in data centers, telecommunications facilities, or industrial environments. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable for various applications, ranging from high-density connections to rugged environments where resilience is paramount.
Network professionals rely on fiber pigtail solutions to create robust and high-performing networks that meet the demands of modern communication systems. As technology continues to advance, the deployment of fiber optic networks will only become more widespread, underscoring the enduring importance of fiber optic pigtails in network deployment.
Future Trends
Staying abreast of evolving trends is crucial for professionals involved in network infrastructure development. In the context of fiber optic networks, future trends are expected to revolve around advancements in connectivity solutions, enhanced performance capabilities, and greater integration with emerging technologies such as 5G and Internet of Things (IoT).
The demand for faster and more reliable data transmission will continue to drive innovation in fiber pigtail technology. This includes developments in connector designs, termination methods, and overall network architecture to meet the escalating requirements of modern communication networks.
Understanding these future trends is vital for network professionals seeking to remain at the forefront of network infrastructure development. By embracing these advancements, they can ensure that their networks are well-equipped to handle the demands of tomorrow's interconnected world.
Insights on Fiber Pigtails
Fiber pigtails, including LC, ST, and SC connectors, are essential components in fiber optic networks. Understanding their applications and significance is crucial for network professionals and enthusiasts. These fiber cable pigtails serve as the vital link between the fiber cables and network equipment, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient data transmission. Their versatility makes them indispensable for various applications, from high-density connections to rugged environments where resilience is paramount. As technology continues to advance, the deployment of fiber optic pigtails will only become more widespread, underscoring their enduring importance in network deployment.
See Also
Simplify Cable Solutions Using Preconn: A Quick On-Site Termination Manual
Discovering the Advantages of the 960 Core Fiber Optic Splice Closure
Revealing the Benefits of Pullable Pre-Connectorized Cables
Advantages of Outdoor Waterproof FastConnect Fiber Field Assembly Connector
Attaining Superior Performance and Cost-Efficient Fiber Optic Connectivity


