How to Choose the Right PLC Splitter for Your PON & FTTx Network
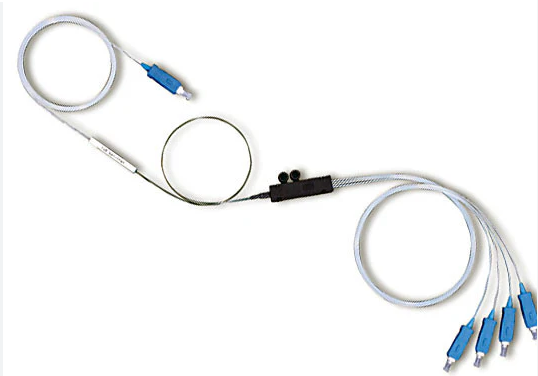
Understanding PLC Splitters
In the world of fiber optic networks, PLC splitters play a crucial role in enabling the efficient distribution and management of optical signals. But what exactly is a PLC splitter, and how does it contribute to the functionality of PON and FTTx networks?
What is a PLC Splitter?
The Basics of Planar Lightwave Circuit Technology
A PLC splitter is a passive optical component that utilizes planar lightwave circuit (PLC) technology to split or combine optical signals. This technology allows for the integration of multiple functional optical devices on a single substrate, resulting in compact and efficient optical components.
Role of PLC Splitters in PON & FTTx Networks
In PON and FTTx networks, PLC splitters serve as key components for splitting or combining optical signals without requiring power input. They are commonly used to divide an incoming optical signal into multiple output signals, allowing network operators to efficiently deliver connectivity to multiple end-users without compromising signal quality.
Benefits of Using PLC Splitters
Low Insertion Loss and High Reliability
One of the primary advantages of PLC splitters is their low insertion loss, which ensures minimal signal attenuation during the splitting process. Additionally, these splitters offer high reliability due to their passive nature, eliminating the need for active components that may be prone to failure.
Efficient Bandwidth Distribution
By leveraging PLC splitters, network operators can effectively distribute bandwidth across multiple end-users within PON and FTTx networks. This enables seamless data transmission and communication services while maintaining optimal network performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a PLC Splitter
When selecting a PLC splitter for your PON or FTTx network, several critical factors should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and seamless connectivity.
Network Requirements
Understanding Your Network's Bandwidth Needs
Before choosing a PLC splitter, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of your network's bandwidth requirements. This involves assessing the volume of data traffic that the network is expected to handle, including both current and future demands. By accurately gauging the bandwidth needs, you can select a PLC splitter with the appropriate split ratio to effectively manage the distribution of optical signals.
Assessing the Number of End Users
Another crucial aspect to consider is the number of end users connected to your network. The PLC splitter selected must be capable of accommodating the anticipated number of end users without compromising signal quality or network performance. By evaluating this factor, you can ensure that each user receives reliable and consistent connectivity without experiencing any degradation in service.
Splitter Configurations and Ratios
Deciding Between Different Split Ratios
The choice of split ratio is a pivotal decision when choosing a PLC splitter. It determines how the incoming optical signal will be divided among multiple output ports. Common split ratios include 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, and 1:16, each catering to specific network requirements. Understanding the distribution needs of your network will guide you in selecting the most suitable split ratio for seamless signal transmission.
The Impact of Configuration on Network Performance
The configuration of a PLC splitter directly influences the overall performance of your network. Opting for an appropriate configuration ensures efficient signal distribution and minimal insertion loss. Careful consideration must be given to how different configurations may affect signal integrity and network reliability, especially as networks evolve and expand over time.
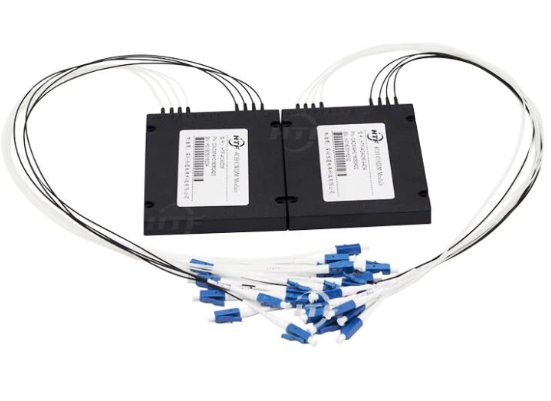

Quality and Reliability
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
Selecting a reputable manufacturer is paramount when choosing a PLC splitter for your network. Established manufacturers with a track record of delivering high-quality passive optical components offer assurance in terms of product reliability and performance. It is advisable to conduct thorough research on manufacturers' credentials and customer feedback before making a selection.
Importance of Testing and Certification
Prioritize PLC splitters that have undergone rigorous testing and certification processes to validate their compliance with industry standards. Certified splitters demonstrate adherence to quality benchmarks, ensuring that they meet stringent performance criteria essential for seamless integration within PON and FTTx networks.
Common Configurations of PLC Splitters
In the realm of PON and FTTx networks, PLC splitters are available in a diverse range of configurations to cater to specific network requirements. Understanding the various configurations and their implications is essential for making informed decisions when selecting a PLC splitter for your network.
Exploring the Varieties
From 1x2 to 2x16: A Comprehensive Overview
PLC splitters come in different configurations denoted by numbers such as 1x2, 1x4, 1x8, 1x16, 2x2, 2x4, 2x8, and 2x16. These numerical representations signify the input and output ports of the splitter. For instance, a 1x4 splitter takes one input and splits it into four outputs. Similarly, a 2x8 splitter accepts two inputs and divides them into eight outputs.
Each configuration serves distinct purposes based on the network's size, topology, and end-user requirements. Smaller configurations like 1x2 or 1x4 are suitable for smaller-scale deployments or point-to-point connections. On the other hand, larger configurations such as 1x16 or 2x16 are ideal for accommodating a more extensive user base within FTTx networks.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Real-world applications demonstrate the practical significance of choosing appropriate PLC splitter configurations. In scenarios where a PON or FTTx network serves a limited number of users within a small geographical area, lower split ratios like 1:4 or even direct point-to-point connections with a ratio of 1:2 may suffice. This ensures that each user receives an adequate portion of the optical signal without compromising signal strength.
Conversely, in densely populated urban areas or multi-dwelling units (MDUs), higher split ratios such as 1:16 or even cascaded splitters may be necessary to accommodate numerous end users while maintaining efficient signal distribution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Network
Matching Configurations to Network Needs
Selecting the most suitable PLC splitter configuration involves aligning it with your network's specific needs and operational objectives. By evaluating factors such as geographical coverage, anticipated user density, and future expansion plans, you can determine the optimal configuration that ensures seamless connectivity while accommodating potential growth.
Consideration should also be given to the type of services being delivered over the network. For instance, if high-bandwidth services like video streaming or cloud-based applications are prevalent within your network infrastructure, opting for higher split ratios may be imperative to sustain consistent service quality across all users.
Considering Future Network Expansions
Anticipating future expansions is crucial when choosing a PLC splitter configuration. As networks evolve to accommodate increasing user demands and technological advancements, scalability becomes paramount. Opting for scalable configurations that allow for easy expansion without significant infrastructure overhauls can mitigate potential disruptions while facilitating seamless integration of additional users or services.
By proactively considering future network expansions during the selection process, you can effectively future-proof your network infrastructure and minimize costly retrofitting efforts down the line.

Installing Your PLC Splitter: Tips and Tricks
As you embark on the installation of a PLC splitter within your PON or FTTx network, careful preparation and methodical execution are essential to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance. This section provides valuable insights into the key considerations, tools required, safety precautions, and a step-by-step installation guide for deploying a PLC splitter effectively.
Preparation and Planning
Tools and Equipment Needed
Before commencing the installation process, it is imperative to gather the necessary tools and equipment to facilitate a smooth deployment. Essential items include fiber optic cleaver, fiber strippers, fusion splicer, fiber connectors, patch cords, cleaning supplies for connectors, cable ties, splice trays, and protective gear such as safety glasses and gloves. Additionally, ensure that you have access to appropriate documentation including network diagrams, specifications for the PLC splitter, and any relevant installation guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
Prioritizing safety measures during the installation of a PLC splitter is paramount to safeguard personnel and prevent damage to optical components. Adhere to industry-standard safety protocols by wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses to shield against potential fiber shards or debris. Exercise caution when handling fiber optic cables to prevent accidental cuts or exposure to harmful elements. Furthermore, maintain a clean work environment free from clutter or obstructions that could pose tripping hazards during the installation process.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Connecting the Splitter to the OLT and ONTs/ONUs
Locate Optimal Placement: Identify an accessible location within your network infrastructure where the PLC splitter can be securely mounted. Ensure that there is adequate space for routing incoming and outgoing fibers without causing strain or bends that could compromise signal integrity.
Prepare Fiber Optic Cables: Carefully strip protective coatings from incoming fibers using fiber strippers while maintaining cleanliness to avoid contamination. Use a fiber cleaver to achieve precise cuts before splicing them with fusion splicers.
Splice Fiber Connections: Employ fusion splicing techniques to create reliable connections between incoming fibers from the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and outgoing fibers leading towards Optical Network Terminals/Units (ONTs/ONUs). Follow industry best practices for fusion splicing including proper alignment of fibers and protection against environmental factors.
Organize Cable Management: Utilize splice trays and cable ties to neatly organize spliced fibers within enclosures or distribution panels. Implement strain relief mechanisms where necessary to prevent excessive tension on delicate fiber connections.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Conduct Optical Power Measurements: Use optical power meters at various points along the network path to verify signal strength consistency before and after passing through the PLC splitter. This ensures that signal loss is within acceptable limits as per network specifications.
Perform End-to-End Testing: Initiate end-to-end testing procedures using OTDR (Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer) or similar testing equipment to validate signal continuity across all connected endpoints including ONTs/ONUs.
Troubleshoot Signal Anomalies: In case of unexpected signal disruptions or irregularities, employ troubleshooting methodologies such as visual inspection of connectors for contamination, re-splicing of fibers if necessary, or verifying alignment in split connections.
Wrapping Up
Key Takeaways
As we conclude our exploration of PLC splitters and their pivotal role in PON and FTTx networks, it's essential to recap the key insights that can guide you in choosing the right PLC splitter for your network infrastructure.
Understanding Network Requirements: Prioritize a comprehensive understanding of your network's bandwidth needs and the number of end users to select a PLC splitter with an appropriate split ratio.
Configurations and Ratios: Carefully consider different split ratios and configurations to ensure seamless signal distribution and accommodate future network expansions.
Quality and Reliability: Emphasize the importance of selecting a reputable manufacturer and prioritizing PLC splitters that have undergone rigorous testing and certification processes.
Further Reading and Resources
For further in-depth knowledge on PLC splitters, PON, FTTx networks, and related optical networking technologies, we recommend exploring the following resources:
Industry Publications: Delve into industry-specific publications, white papers, and technical journals that offer detailed insights into the latest advancements in passive optical components and network architectures.
Manufacturer's Documentation: Refer to documentation provided by reputable manufacturers offering PLC splitters to gain specific product details, installation guidelines, and best practices for optimizing performance.
Online Forums and Communities: Engage with professionals within online forums or communities dedicated to fiber optic networking to exchange experiences, seek recommendations, and stay updated on emerging trends.
By leveraging these resources, you can enhance your knowledge base, stay informed about industry best practices, and make well-informed decisions when selecting, installing, or maintaining PLC splitters within your optical network infrastructure.
In conclusion, choosing the right PLC splitter involves a meticulous evaluation of network requirements, thoughtful consideration of configurations, and a commitment to quality assurance. With a clear understanding of these aspects coupled with thorough research from credible sources, you can effectively optimize your PON or FTTx network for seamless connectivity while laying a robust foundation for future scalability.
See Also
Simplify Cable Solutions Using Preconn: A Quick On-Site Termination Guide
ADSS Fiber Cable vs. Alternative Cables: Selecting the Best Choice for Long Span Uses
Discovering the Revolutionary Precon Cabling Solution
Uncovering the Advantages of IP67 Waterproof FTTX Solutions
Durable Outdoor Connectivity: OptiTap's Waterproof FTTA Patch Cord


